Archives
- 2025-12
- 2025-11
- 2025-10
- 2025-09
- 2025-03
- 2025-02
- 2025-01
- 2024-12
- 2024-11
- 2024-10
- 2024-09
- 2024-08
- 2024-07
- 2024-06
- 2024-05
- 2024-04
- 2024-03
- 2024-02
- 2024-01
- 2023-12
- 2023-11
- 2023-10
- 2023-09
- 2023-08
- 2023-07
- 2023-06
- 2023-05
- 2023-04
- 2023-03
- 2023-02
- 2023-01
- 2022-12
- 2022-11
- 2022-10
- 2022-09
- 2022-08
- 2022-07
- 2022-06
- 2022-05
- 2022-04
- 2022-03
- 2022-02
- 2022-01
- 2021-12
- 2021-11
- 2021-10
- 2021-09
- 2021-08
- 2021-07
- 2021-06
- 2021-05
- 2021-04
- 2021-03
- 2021-02
- 2021-01
- 2020-12
- 2020-11
- 2020-10
- 2020-09
- 2020-08
- 2020-07
- 2020-06
- 2020-05
- 2020-04
- 2020-03
- 2020-02
- 2020-01
- 2019-12
- 2019-11
- 2019-10
- 2019-09
- 2019-08
- 2019-07
- 2019-06
- 2018-07
-
Muscle Ring Fingers MuRFs comprising TRIM MuRF TRIM MuRF and
2021-05-28
Muscle Ring Fingers (MuRFs) comprising TRIM63 (MuRF1), TRIM55 (MuRF2) and TRIM54 (MuRF3) are the most studied TRIMs in the heart. However, with increasing knowledge of E3 ligases and recent advancements in the field, many other TRIMs such as TRIM8, TRIM21, TRIM24, TRIM32, TRIM45, TRIM69 and TRIM72 w
-
Introduction Protein ubiquitination is a posttranslational m
2021-05-28
Introduction Protein ubiquitination is a posttranslational modification that plays a major role in almost all cellular processes in eukaryotes (Hochstrasser, 2009; Komander & Rape, 2012). It involves the covalent attachment of ubiquitin (Ub) via its C-terminal glycine carboxylate to a primary amine
-
In the present work we have investigated the reactivity
2021-05-28
In the present work, we have investigated the reactivity of N-aryl-N′-hydroxyguanidines 1a–d (see Scheme 1 for structures) with the water-soluble Cu(II) complex 8. Using EPR and UV–Visible spectroscopy, we have shown that the studied N-aryl-N′-hydroxyguanidines 1a–d can bind and transfer electrons t
-
The CysLT receptor antagonist BayCysLT RA significantly supp
2021-05-28
The CysLT2 receptor antagonist BayCysLT2RA significantly suppressed multiple antigen challenge-induced infiltration of eosinophils and mononuclear HOSu into the lung, indicating that CysLT2 receptor activation is involved in leukocyte migration. In contrast to the present finding, Barret et al. [21
-
In the present study we identified that SDF could significan
2021-05-28
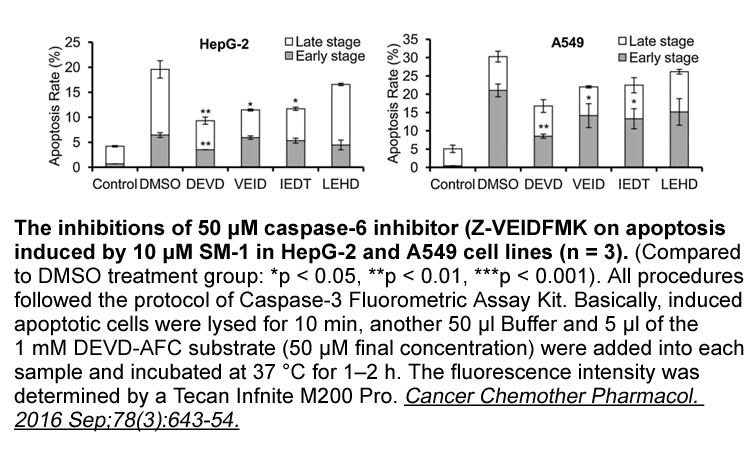
In the present study, we identified that SDF-1α could significantly elevate the expression of p-P65 in the NF-κB signaling pathway and p-Akt in the PI3K-Akt signaling pathway, while significantly reducing the expression of p-IκB in the NF-κB signaling pathway. AMD3100 and hesperidin antagonized the
-
We have previously characterized the leucine rich
2021-05-28

We have previously characterized the leucine-rich NESs located within the zinc-binding domains of mucosal high risk HPV16 E7 (76IRTLEDLLM84) and low risk HPV11 E7 (76IRQLQDLLL84) mediating their nuclear export in a CRM1 dependent manner (Knapp et al., 2009, McKee et al., 2013). The zinc-binding doma
-
In the case of ionic liquids the association scheme should
2021-05-27
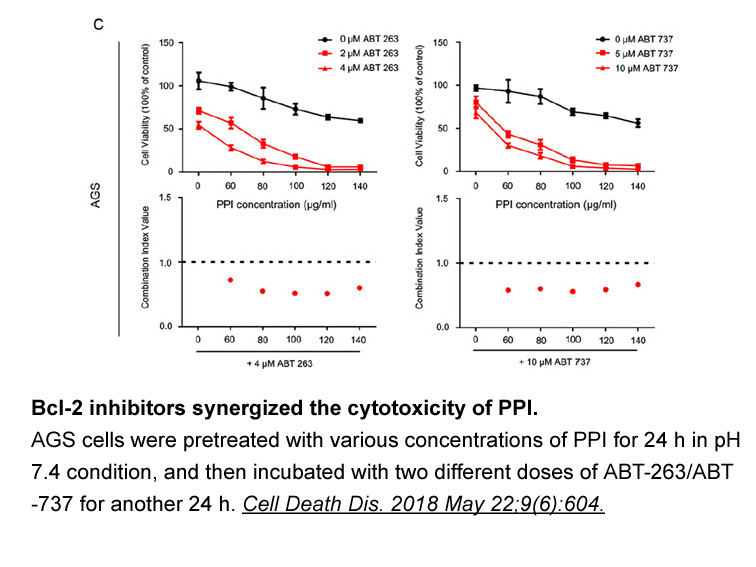
In the case of ionic liquids, the association scheme should be determined and considered for calculations. H. Soltani Panah (2017) suggested the 2B scheme for the imidazolium-based ionic liquids. His speculation has been used in this study for the modeling [22]. Considering 2B association scheme, th
-
br Materials and methods br Results br
2021-05-27
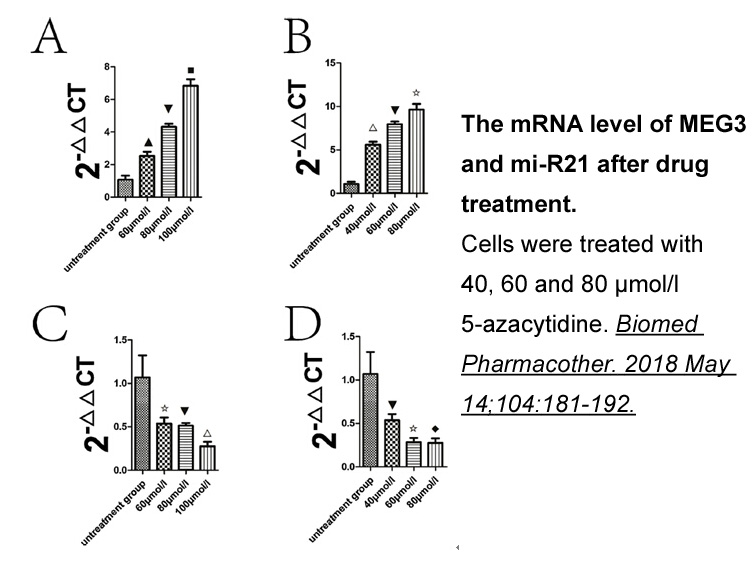
Materials and methods Results Discussion Prolyl 4-hydroxylases are oxygenases with key roles in a variety of biological processes including oxygen sensing, siRNA regulation and collagen folding (Gorres and Raines, 2010). Hydroxyproline is particularly abundant in collagenous proteins which
-
A widely accepted mechanism to differentiate hESCs into
2021-05-27
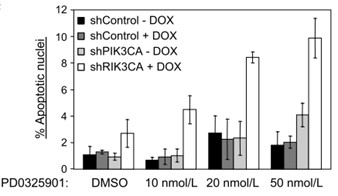
A widely accepted mechanism to differentiate hESCs into cardiomyocytes is through perturbation of the canonical Wnt/β-catenin pathway. Initial Wnt activation is required to form the MK-8669 [3]. Thereafter, it is believed that inhibition of the canonical Wnt/β-catenin pathway is pivotal for cardiom
-
NPC L NPC Niemann Pick C like like
2021-05-27
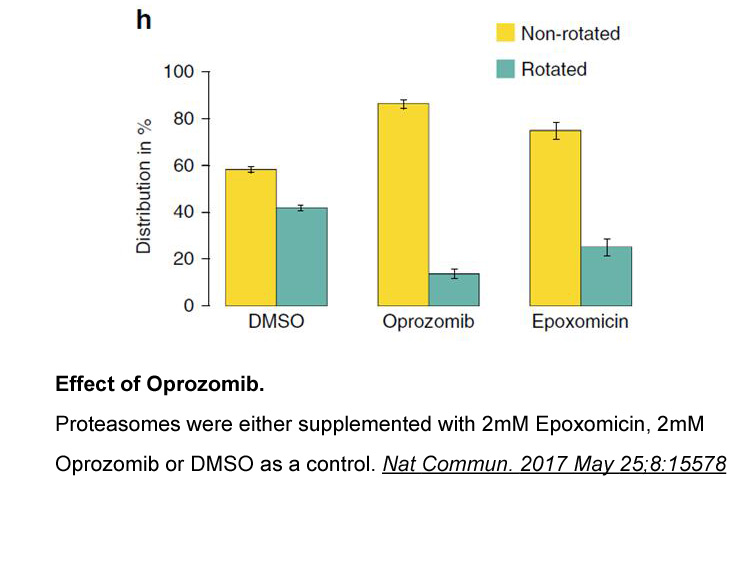
NPC1L1 (NPC1 [Niemann-Pick C-like-1]-like intracellular cholesterol transporter) is the rate-limiting transmembrane transporter for cholesterol Liraglutide mg from the intestinal lumen, and it mediates the absorption of both dietary and biliary cholesterol., , NPC1L1 is the target of the cholester
-
Current therapeutic protocols in OS
2021-05-27
Current therapeutic protocols in OS and ES consist of neoadjuvant chemotherapy and local surgical resection, followed by adjuvant chemotherapy. These treatments lead to a 70% overall survival for localized disease but can decrease to 15% in case of metastasis. With CS being resistant to conventional
-
CAY10603 Although BPA has been proven to cause
2021-05-27

Although BPA has been proven to cause many health issues such as obesity and neurological toxicity (Rubin, 2011), the effects and mechanisms of BPA on the human tumorigenesis and cancer development are still not well illustrated. In the present study, we found that 10 to 10M BPA significantly promot
-
br The orphan estrogen related receptor
2021-05-27
The orphan estrogen-related receptor exists as three subtypes (ERRα, ERRβ, and ERRγ) in the human genome. ERRα is expressed in metabolically active tissues such as muscle and adipose. ERRγ is expressed in the spinal cord and CNS. ERRβ appears to play a role in development, as postnatal expression
-
The acid base properties of the
2021-05-27
3. The acid-base properties of the IL are important issues to consider because protonation changes caused by Brønsted-acidic or basic ions may result in enzyme deactivation [29]. Thereby, the acid-base properties of the newly designed IL need proper control for enzymes by selection of appropriate ca
-
Another interesting finding regarding substrate selectivity
2021-05-27

Another interesting finding regarding substrate selectivity of iPLA2-VIA in whole cellular systems stems from the observation that some of the major species hydrolyzed by the enzyme contain a 16:1 fatty Pepstatin A at the sn-2 position [57,119], raising the possibility that iPLA2-VIA may constitute
14879 records 637/992 page Previous Next First page 上5页 636637638639640 下5页 Last page